Solar energy is simple. When sunlight hits photovoltaic (PV) solar panels, electrons are knocked free to move around in the electric field created between layers of silicon. Once installed, most solar panels can produce emission-free electricity for over 30 years. When it is generated, solar electricity comes in the form of direct current (DC). Most homes utilize alternating current (AC), which allows appliances of various voltages to be plugged into residential electric outlets. For this reason, solar energy is typically sent through an inverter which modifies the wave from DC to usable AC.

Grid Tie
Solar Power
Systems
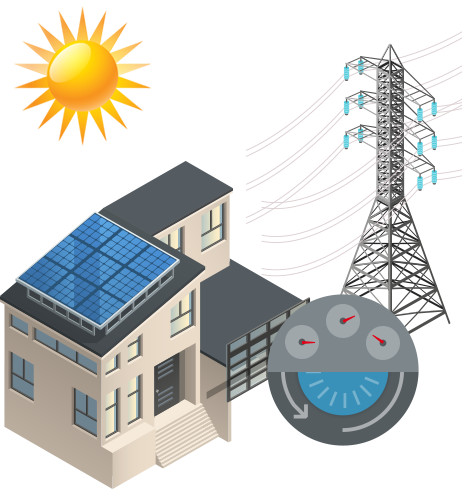
Today, most homes in the United States looking to go solar will install a grid-tied system. In a grid tie solar system, excess energy generated from the solar panels is fed back into the grid. In Florida, you can be credited for the electricity that you produce and send to the grid. For most, homeowners with grid tie solar systems will only need to pay an electric bill when their monthly electricity consumption exceeds their solar panel’s production.
Off Grid
Solar Power
Systems
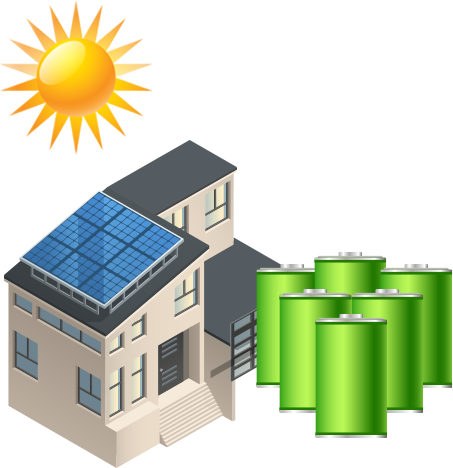
In some cases, home and business owners may want to consider a solar energy system with an added storage capacity. Off grid solar power is made possible by storing all of the energy generated by an array of solar panels in a battery or battery bank. Here, the possibilities are endless, as an off grid solar power system can produce and use electricity anywhere the sun shines.
Hybrid
Solar Power
Systems
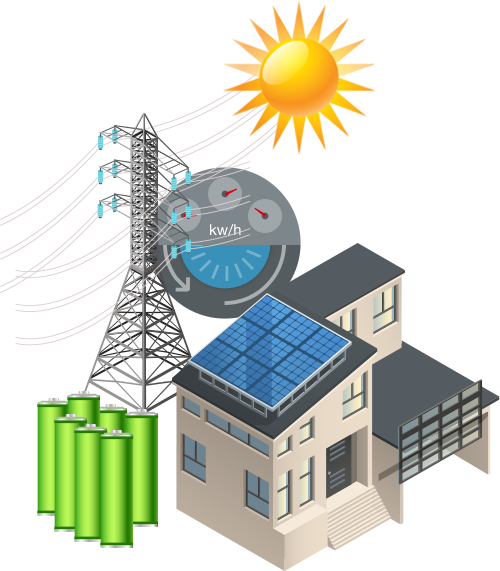
Lastly, A hybrid solar power system is a grid tie installation with a battery backup. In a lot of homes and businesses, solar storage can be a bit too expensive to see a strong financial return on investment. However, in both areas prone to grid outages and unfavorable solar metering policies, a battery-backed, grid-tie system may be the best option.